AUGMENT® Bone Graft Clinical Evidence

“These three papers changed my clinical practice.”
DR. GREGORY BERLET
Westerville, OH
 DiGiovanni CW, et al. Recombinant Human Platelet-Derived Growth Factor-BB and Beta-Tricalcium Phosphate (rhPDGF-BB/β-TCP): An Alternative to Autogenous Bone Graft. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013 Jul 3;95(13):1184-92. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.K.01422. PubMed PMID: 23824386.*
DiGiovanni CW, et al. Recombinant Human Platelet-Derived Growth Factor-BB and Beta-Tricalcium Phosphate (rhPDGF-BB/β-TCP): An Alternative to Autogenous Bone Graft. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013 Jul 3;95(13):1184-92. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.K.01422. PubMed PMID: 23824386.*
*FDA did not base its approval of AUGMENT® Bone Graft on radiologic findings from the pivotal study, but instead relied on clinical outcomes
 AUGMENT® Regenerative Solutions is composed of recombinant human protein, platelet-derived growth factor-BB or rhPDGF-BB, combined at the time of surgery with β-TCP (1000-2000um) granules. Bone fusion requires three fundamental factors for success: scaffold, cells, and signals. AUGMENT® provides the signals and scaffold for successful bone fusion. Cells are recruited from the patient by the rhPDGF-BB, and the β-TCP is the scaffold which facilitates delivery of rhPDGF-BB and acts as an osteoconductive matrix for bone repair.
AUGMENT® Regenerative Solutions is composed of recombinant human protein, platelet-derived growth factor-BB or rhPDGF-BB, combined at the time of surgery with β-TCP (1000-2000um) granules. Bone fusion requires three fundamental factors for success: scaffold, cells, and signals. AUGMENT® provides the signals and scaffold for successful bone fusion. Cells are recruited from the patient by the rhPDGF-BB, and the β-TCP is the scaffold which facilitates delivery of rhPDGF-BB and acts as an osteoconductive matrix for bone repair.
Platelet-Derived Growth Factor (PDGF) is a naturally occurring protein which is released by platelets during the earliest phases of healing. PDGF recruits cells to the site of injury through chemotaxis, and multiplies those cells through mitogenesis. These cells then respond to PDGF and other growth factors to differentiate into callus. The callus is infiltrated by vasculature which is facilitated by the pro-angiogenic effect of PDGF and the upregulation of VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor). This, in turn, stimulates the body’s bone healing cascade and the callus is transitioned into hard callus made of endochondral bone. The bone is remodeled over time through the balanced activity of osteoblasts and osteoclasts. It is important to note that PDGF is one of the primary factors released in response to injury, and this mechanism of action is a key to recruiting mesenchymal stem cells(MSC) which can ultimately differentiate into osteoblasts at the injury site. In the arthrodesis patient, this ability for PDGF to impact healing at the earliest stages is of critical importance.
Independent peer-reviewed literature has shown that rhPDGF-BB, the recombinant form of naturally-occurring PDGF, has the same functionality, potency and specificity as endogenous (natural) PDGF. PDGF is naturally expressed by the body as a part of the healing process, as shown in the chart below. PDGF is expressed by the body early in the healing process during hematoma formation and inflammation processes. PDGF has a secondary effect that occurs toward the final stages of the bone repair/healing process through newly formed blood vessels (angiogenesis) and the remodeling of bone.
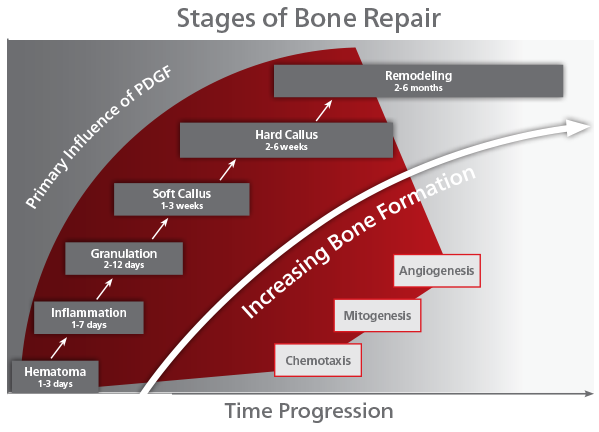
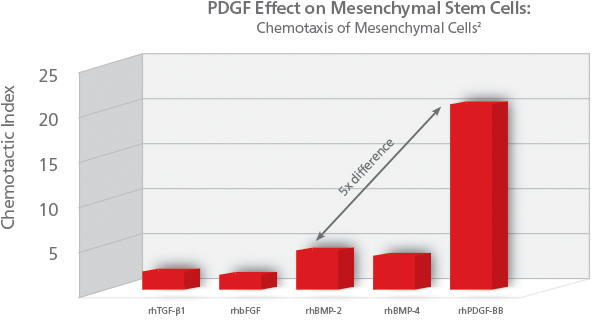
PDGF is called a chemotactic agent, because its presence initiates recruitment of cells to the bone graft site for healing (chemotaxis). Specifically for PDGF, it signals mesenchymal stem cells to migrate to the healing site. Mesenchymal stem cells are precursors to osteoblasts and other important cells in bone healing. PDGF is the most potent chemotactic agent for cells of mesenchymal origin, over 5x more potent than rhBMP-2. PDGF’s chemotactic properties help ensure the presence of cells needed for bone healing and growth.
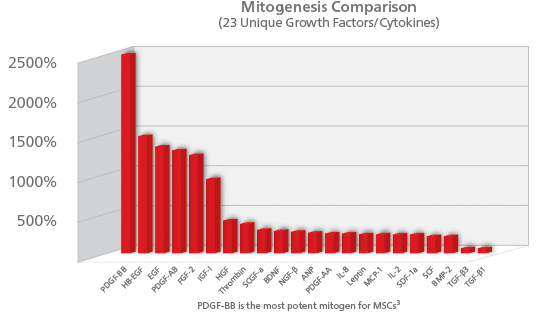
PDGF also helps foster bone growth by stimulating the proliferation of bone cells (mitogenesis). When a cell undergoes mitogenesis, it divides in two to create two exact copies of the original cell. PDGF is the most potent signal for mitogenesis. In Ozaki (2007) PDGF-BB was shown to be the most potent mitogen of 23 growth factors studied in a rabbit model.
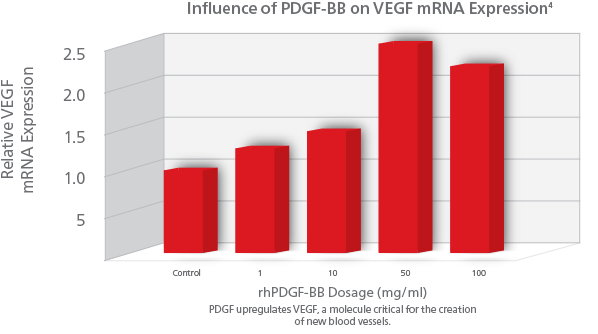
PDGF also signals for the formation of vasculature needed to support new bone growth (angiogenesis). PDGF’s presence signals production of a factor called vascular endothelial growth factor(VEGF), which is a growth factor that stimulates formation of new blood vessels. New blood vessels assure the continued supply of cells to the wound, supporting ongoing healing and bone remodeling. rhPDGF-BB stimulates angiogenesis by upregulating VEGF creating an environment for healing and cellular differentiation.
References
1. DiGiovanni C, Lin S, Pinzur M. Recombinant human PDGF-BB in foot and ankle fusion. Expert Rev Med Devices 2012 Mar 9 (2):111-22.
*FDA did not base its approval of AUGMENT® on radiologic findings from the pivotal study, but instead relied on clinical outcomes.
2. Fiedler J, et al. BMP-2, BMP-4, and PDGF-bb stimulate chemotactic migration of primary human mesenchymal progenitor cells. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry 2002.
3. Ozaki Y, et al. Comprehensive Analysis of Chemotactic Factors for Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Stem Cells and Development, Volume: 16 Issue 1: March 11, 2007.
4. Bouletreau P, et al. Factors in the fracture microenvironment induce primary osteoblast angiogenic cytokine production. Plast Reconstr Surg 2002 Jul;110(1):139-48
Recent Clinical Evidence
DiGiovanni CW, Lin SS, Daniels TR, Glazebrook M, Evangelista P, Donahue R, Beasley W, Baumhauer JF. The Importance of Sufficient Graft Material in Achieving Foot or Ankle Fusion. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2016 Aug 3;98(15):1260-7. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.15.00879. PMID: 27489316. Read more
Glazebrook M, Beasley W, Daniels T, Evangelista PT, Donahue R, Younger A, Pinzur MS, Baumhauer JF, DiGiovanni CW. Establishing the relationship between clinical outcome and extent of osseous bridging between computed tomography assessment in isolated hindfoot and ankle fusions. Foot Ankle Int. 2013 Dec;34(12):1612-8. doi: 10.1177/1071100713504746. Epub 2013 Sep 16. PubMed PMID: 24043351. Read more
This map shows the clinical investigator members that participated in the North American Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Study Group.
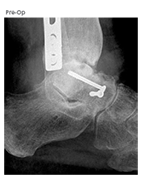
Case Report 1: Subtalar Fusion using AUGMENT® Bone Graft: 62 YO Female
As presented by Mark Glazebrook, MD
Assoc Professor of Orthopedic Surgery, Dalhousie University, Past-COFAS President
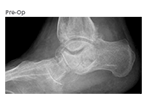
Case Overview
- The patient is a 62 year old female who presented with a painful hindfoot that worsened when walking on uneven surfaces
- History of rheumatoid arthritis assesed with osseous defects from pathology or traumatic injury
- Baseline reported AOFAS total score of 2, FFI score of 51, and SF-12 Quality of Life PCS score of 22
- Pre-op X-Ray and CT scans demonstrated severe arthritic degeneration of subtalar joint
Operative Treatment Plan
- Subtalar arthrodesis ORIF using AUGMENT® Bone Graft
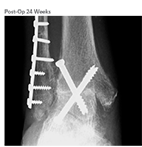
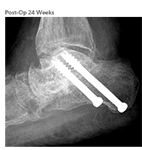
Clinical Outcome
- Patient was non weightbearing with immobilization for 6 weeks post-op, progressive weight-bearing thereafter
- Radiographic union at 24 weeks and after as determined by the surgeon
- At 12 months, improved to a final AOFAS Score of 84, FFI score of 11, and SF-12 Quality of Life PCS score of 53
Case Report 2: Tibiotalar Fusion using AUGMENT® Bone Graft: 80 YO Female
As presented by Mark Glazebrook, MD
Assoc Professor of Orthopedic Surgery, Dalhousie University, Past-COFAS President
Case Overview
- Post-Traumatic Injury/Deformity
- Osteopenia
- Intense Pain at Fusion Site
Operative Treatment Plan
- Tibiotalar Fusion using AUGMENT® Bone Graft
Clinical Outcome
- Patient was non weightbearing with immobilization for 6 weeks post-op, progressive weight-bearing thereafter
- Radiographic union at 24 weeks and after as determined by the surgeon
- At 12 months, improvement to site pain assessment on VAS from 88mm to 29mm (Δ59)
Case Report 3: Tibiotalar Fusion: 62 YO Male
As presented by Mark Glazebrook, MD
Assoc Professor of Orthopedic Surgery, Dalhousie University, Past-COFAS President
Case Overview
- Post-Traumatic Injury/Deformity
- 62 year old male with painful ankle joint
- History of alcohol abuse
- Patient has history of joint mal-alignment with osseous defects from pathology or traumatic injury
- Cirrhosis of the liver
- BMI = 34
- Baseline reported weight-bearing pain of 46mm (100mmVAS scale), Foot Function Index score of 59 and SF-12 Quality of Life PCS score of 29
Operative Treatment Plan
- Ankle arthrodesis ORIF using AUGMENT® Bone Graft
Clinical Outcome
- Patient was non-weight bearing with immobilization for 6 weeks post-op, progressive weight-bearing thereafter
- Radiographic union at 24 weeks and after as determined by the surgeon
- At 12 months, improvement to weight bearing pain of 1mm (Δ45), FFI of 1 (Δ59) and SF-12 PCS of 48 (Δ20)
FDA did not base its approval of AUGMENT® on radiologic findings from the clinical trial(s), but instead relied on clinical outcomes.
Indications For Use
AUGMENT® Bone Graft and AUGMENT® Injectable are indicated for use as an alternative to autograft in arthrodesis (i.e., surgical fusion procedures) of the ankle (tibiotalar joint) and/or hindfoot (including subtalar, talonavicular, and calcaneocuboid joints, alone or in combination), due to osteoarthritis, post-traumatic arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, avascular necrosis, joint instability, joint deformity, congenital defect, or joint arthropathy in patients with preoperative or intraoperative evidence indicating the need for supplemental graft material.
Contraindications
AUGMENT® Bone Graft and AUGMENT® Injectable should not:
- be used in patients who have a known hypersensitivity to any of the components of the product or are allergic to bovine collagen (AUGMENT® Injectable only) or yeast-derived products.
- be used in patients with active cancer.
- be used in patients who are skeletally immature (<18 years of age or no radiographic evidence of closure of epiphyses).
- be used in pregnant women. The potential effects of rhPDGF-BB on the human fetus have not been evaluated.
- be implanted in patients with an active infection at the operative site.
- be used in situations where soft tissue coverage is not achievable.
- be used in patients with metabolic disorders known to adversely affect the skeleton (e.g. renal osteodystrophy or hypercalcemia), other than primary osteoporosis or diabetes.
- be used as a substitute for structural graft.
WARNINGS
As with all therapeutic recombinant proteins, there is a potential for immune responses to be generated to the rhPDGFBB component of AUGMENT® Bone Graft and AUGMENT® Injectable. The immune response to rhPDGF-BB was evaluated for AUGMENT® Injectable in two studies, and for AUGMENT® Bone Graft (which contains the identical rhPDGF-BB) in two pilot and one pivotal study for ankle and hindfoot arthrodesis procedures. The detection of antibody formation is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Additionally, the observed incidence of antibody (including neutralizing antibody) positivity in an assay may be influenced by several factors including assay methodology, sample handling, timing of sample collection, concomitant medications, and underlying disease. For these reasons, comparison of the incidence of antibodies to AUGMENT® Bone Graft or AUGMENT® Injectable with the incidence of antibodies to other products may be misleading.
Women of childbearing potential should avoid becoming pregnant for one year following treatment with AUGMENT® Bone Graft or AUGMENT® Injectable. The implantation of rhPDGF-BB in women and the influence of their development of anti-PDGF-BB antibodies, with or without neutralizing activity, on human fetal development are not known.
The safety and effectiveness of AUGMENT® Bone Graft or AUGMENT® Injectable in nursing mothers has not been established. It is not known if rhPDGF-BB is excreted in human milk.
The safety and effectiveness of AUGMENT® Bone Graft or AUGMENT® Injectable has not been established in anatomical locations other than the ankle or hindfoot, or when combined with autologous bone or other bone grafting materials.
The safety and effectiveness of repeat applications of AUGMENT® Bone Graft or AUGMENT® Injectable have not been established.
The safety and effectiveness of AUGMENT® Bone Graft or AUGMENT® Injectable in pediatric patients below the age of 18 years have not been established.
AUGMENT® Bone Graft or AUGMENT® Injectable do not have any biomechanical strength and must be used in conjunction with standard orthopedic hardware to achieve rigid fixation.
The β-TCP component is radiopaque, which must be considered when evaluating radiographs for the assessment of bridging bone. The radiopacity may also mask underlying pathological conditions. Over time, the β-TCP is intended to be resorbed at the fusion site and replaced by new bone. Under such circumstances, it would typically be indistinguishable from surrounding bone.
Please refer to the full package insert for more information:
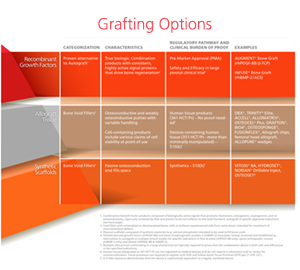
With the myriad of bone graft options available and continuing to grow, it has become increasingly difficult for surgeons and hospitals to avoid confusion and maintain a clear understanding of the clinical value, specific features, benefits, and appropriate uses of available graft choices.
To make the best graft selection, it is good to ask the following questions:
- How was it approved?
- How should it be used?
- How does it work?